What is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer or hepatic cancer are two types of primary and secondary.
That is, if the root of this disease is in the liver, it spreads to primary and other organs, it is called secondary cancer. Secondary cancer is more common than primary.
Cancer arises from unusual growth of cells.
Despite the harmful effects of cancer, the liver continues to function regularly in the body, so cancer is not noticed for a long time.
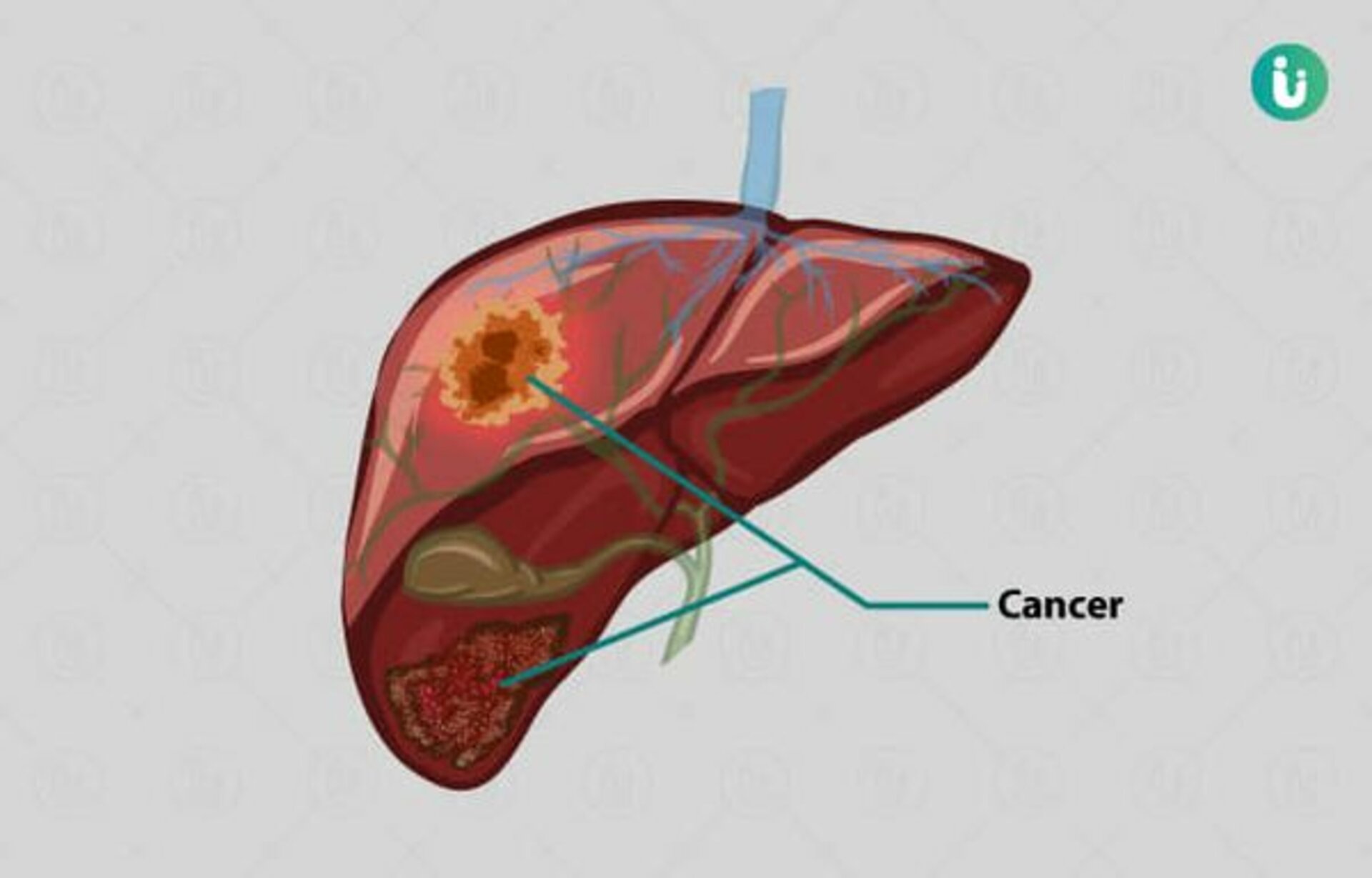
- Primary liver cancer contains hepatosellular carcinoma.
Fibrolamellar cancer.
Intrahepatic colangiocarcinoma.
Liver angiosarcoma.
Hepatoblastoma.
Primary liver is not diagnosed with cancer for a long time as stated above, its symptoms may be as follows
Losing weight without a reason.
Feeling full even when food is short.
Loss of appetite.
Vomiting.
Jaundice (yellow eyes, nails and urine).
Pain or swelling in the area near the abdomen.
Weakness.
Itching to the skin.
What's the main thing to do with this?
Organ failure causes liver cancer due to the following reasons:
- Syrhosis in which alcoholism has adverse effects on liver tissues.
- Hepatitis virus bc or d.
- Arsenic exposure.
- Smoking.
- Diabetes.
- Secondary bowel or chest cancer.

How is it diagnosed and treated?
- Blood test to check liver function.
- Biopsy of the liver.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scan.
- The endoscopy of the abdomen.
- CT scan.
- Ultrasound.
- Laproscopy.
A review every 3 months is sufficient for injuries smaller than a centimeter. In some cases, surgery is sufficient to heal the damage of liver cells as well as for reproductive growth.
The treatment of liver cancer depends on the amount and form of cancer.
The treatment of liver cancer depends on the amount and form of cancer. Here are the following options available for that:
Surgery to remove useless cells and affected parts.
Liver transplant.
Chemotherapy
Embolization therapy (for those who cannot perform surgery for some medical reasons).
Targeting therapy to prevent cell growth.
Having Stomach Disorder or Digestive Problems